1º de ESO Geography and History
 Unit EGYPT-Index Unit EGYPT-Index
GEOGRAPHIC LOCATION
ECONOMY
SOCIETY
GOVERNMENT
WRITING and CULTURE
RELIGION
ART
 MIND MAPS MIND MAPS

 Mind map Mind map |
 GLOSSARY GLOSSARY
Civil Servant
Colossal (Arte)
Column
Grave goods
Lintel
Scribe
Surplus
 EXERCISES EXERCISES
 ACTIVITIES ACTIVITIES
 LINKS LINKS
 KEYWORDS KEYWORDS
 USUAL PHRASES USUAL PHRASES
 Unit THE EARTH PLANET Unit THE EARTH PLANET
 Unit RELIEF Unit RELIEF
 Unit THE CLIMATE Unit THE CLIMATE
 Unit PREHISTORIC LIFE Unit PREHISTORIC LIFE
|
Bilingual Space  |
 Egyptian religion was polytheistic, that is, they believed in various gods and goddesses, not in just one. Egyptian religion was polytheistic, that is, they believed in various gods and goddesses, not in just one. |
|
 
Isis y Osiris
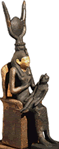
Isis and Orus
|
The deities had a half human (anthropomorphic) appearance, half animal (zoomorphic). They had several rituals, the most important of which was dedicated to favoring the wishes of the rising of the Nile River, which was very necessary for agriculture.
At the service of religion, we could find priests, who had great power, accumulating great wealth in their temples, and they were owners of a large part of the country's land.
 Sarcophagus
Sarcophagus
|
|
The Egyptians thought that there was life after death, or in other words, an
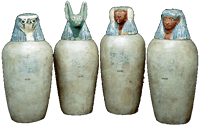 Canopics jarr Canopics jarr |
afterlife. The dead were buried in tombs (pyramids, mastabas, or hypogeum), some of which had rich graves goods. Thanks to that, we know a great deal about their civilization. |
A product of the belief in the afterlife was mummification, or the  preparation of the dead for the next life. The bodies were subjectedto a long process during which their intestineswere extracted (and deposited in glasses called “canopic jars”) and, through the coated in different substances, they were carefully wrapped in bandage to preparation of the dead for the next life. The bodies were subjectedto a long process during which their intestineswere extracted (and deposited in glasses called “canopic jars”) and, through the coated in different substances, they were carefully wrapped in bandage to 
preserve the appearance they had when they were alive.
|
|
| |

Usamos cookies propias y de terceros que entre otras cosas recogen datos sobre sus hábitos de navegación para mostrarle publicidad personalizada y realizar análisis de uso de nuestro sitio.
Si continúa navegando consideramos que acepta su uso. OK Más información
© Jorge
Juan Lozano Cámara, profesor del IES
Juan de la Cierva de Vélez-Málaga
Licenciado por la Universidad de Granada (España) 
Eduardo Gallardo Téllez, profesor del IES Juan
de la Cierva de
Vélez-Málaga
Licenciado por la Universidad de Málaga (España) 
Ana María Marcos Sánchez, profesora del IES Juan de la Cierva de Vélez-Málaga
Licenciada por la Universidad de Málaga (España)
Kerry Elyse Hart, Licenciada por la Universidad de Richmond (Virginia, USA)
|
|

